Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
A total hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus and cervix. This operation is one of the most common in gynecological practice. The procedure can be lifesaving for those suffering from heavy bleeding due to fibroids, adenomyosis or severe pain due to Endometriosis or gynecological cancers. A hysterectomy is a major surgery, but with new technological advances, the discomfort, risk of infection, and recovery time has all been decreased remarkably.What are the types of hysterectomy?
- Open, traditional Hysterectomy: This involves a six to eight-inch incision made in the abdominal wall.
- Vaginal Hysterectomy: This involves removing the uterus through the vagina. This approach is better than the open, traditional hysterectomy, but still does not allow the surgeon a full view of the surrounding organs, including the bladder & ureter.
- Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy.
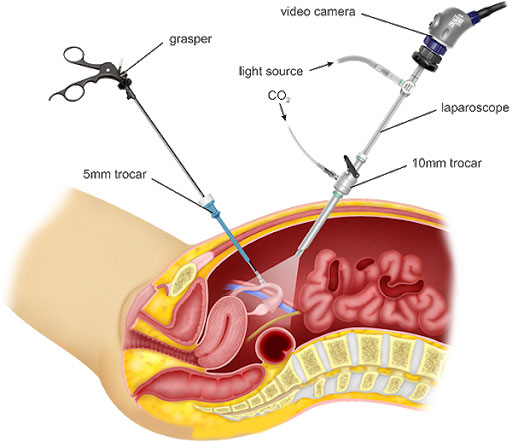
What is total laparoscopic hysterectomy?
Using a laparoscope, a slender, fibre-optic tube equipped with a miniature camera, lights and surgical instruments, gynaecologists have the ability to see inside the abdomen and technical access to the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes without having to make a large incision. The duration of total laparoscopic hysterectomy varied 40-80 minutes (average 60 minutes). With advanced laparoscopic skills, gynaecological surgeons are able to perform TLH. The surgery is completed utilizing only four tiny abdominal incisions 5mm to 1cm long. Even a very large uterus can be removed laparoscopically using this technique. It offers numerous potential benefits over traditional approaches, particularly when performing more challenging procedures like radical hysterectomy for gynaecologic cancer.
What are the indications of hysterectomy?
- Removal of fibroids, which are noncancerous tumours
- Cases of abnormal uterine bleeding
- Treatment of endometriosis, the growth of the uterine lining outside of the uterus
- Resolve uncontrolled bleeding caused by adenomyosis, cancer or pelvic organ prolapse
- Less blood loss
- Fewer complications
- Less scarring
- Decreased risk of infection

