Fertility Enhancing
Surgeries
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries
Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy are the surgeries performed for enhancing fertility.
LAPAROSCOPY
Laparoscopy is a surgical procedure in which a thin, lighted tube known as laparoscope is put through an incision in the belly to check the abdominal organs or female pelvic organs. Through this incision, the tissue sample is collected for biopsy.
Why is Laparoscopy done?
It is done for the diagnosis of below conditions that make the natural conception difficult for a woman:
- Related to cysts
- Adhesions
- Fibroids
- Infections
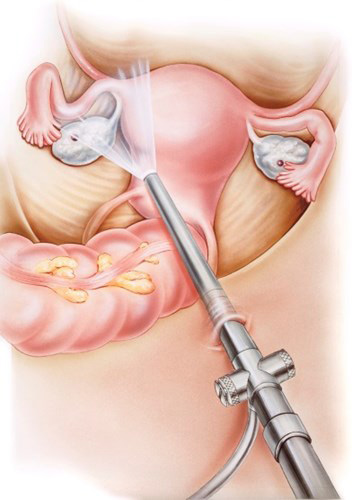
Laparoscopy is done for below fertility treatment procedures like:
- Cysts removal
- Fibroid
- Tubal recanalization
- Drainage of fluid filled in tubes
- Occluding the tubes in cases of hydrosalpinx
- Drilling the ovary in PCOS
- Removal of adhesions.
How is Laparoscopy done?
Laparoscopy is a 30-90 minutes procedure and is usually done under a general anesthesia. In some cases, the surgeon may recommend spinal anaesthesia. A small incision is made in the belly. Through this incision, a hollow needle is put, through which gas (carbon dioxide or nitrous oxide) is slowly released in the belly to inflate the belly, so the abdominal wall lifts away from the organs inside for a clearer view for the surgeon.
A thin, lighted tube known as the laparoscope is then put through the incision to look at the internal organs. A laser may be attached to the laparoscope to assist the surgery.
Once the surgery is completed, the gas is released from the belly and the incisions are sutured and covered with a bandage. The scars are very small and fade away over time.
Recovery after Laparoscopy
The patient is kept under observation for 2-4 hours. You may resume normal day to day activities next day after surgery. However, strenuous activities and exercises should be avoided for 1 week. You may experience some bloating & bruising around the incision for few days.
HYSTEROSCOPY
Hysteroscopy procedure is done using a thin viewing tool known as hysteroscope to look at the lining of the uterus. The hysteroscope has a light and a camera attached to it, through which the doctor can see the uterus lining on the video screen.
The tip of the hysteroscope is inserted into the vagina and gently moved into the uterus through the cervix.
Why is Hysteroscopy done?
It is done in women who have infertility issues to:
- Evaluate the uterine lining
- Manage tubal blocks
- Remove intrauterine polyps, fibroids
- Break adhesions in the uterine cavity
How is Hysteroscopy done?
Hysteroscopy is a short day care procedure and is done using sedatives or anaesthesia. The patient is asked to empty the bladder before the test. The doctor will insert a lubricated tool, speculum into the vagina, which gently spreads apart the vaginal walls for the doctor to see inside the vagina and the cervix.
The hysteroscope will be placed at the entrance of the vagina and gently moved into the uterus through the cervix. The doctor will then put gas or liquid through the hysteroscope into the uterus for a clearer view of the uterus lining. Video screen may be used by the doctor.
Recovery after Hysteroscopy
After the Hysteroscopy procedure, the patient will be monitored in the recovery room for 1-4 hours. Most patients go home on the same day of the procedure and in very rare cases, you may be advised to stay at the facility overnight.
It is normal to have some vaginal bleeding for 1-2 days post hysteroscopy. You may experience slight dizziness, stomach sickness or mild belly pain. These are temporary and should go away in 24 hours.
In case of infertility, Laparoscopy is often performed along with Hysteroscopy as the indication may be.

